
The manufacturing industry is constantly evolving and changing with new technologies coming out every day. This article looks at the top 5 fabrication technologies that are predicted to change the industry in the next 5 years.
1. Additive Manufacturing
Additive Manufacturing (AM) is a process of making three-dimensional solid objects from a digital file. The creation of a 3D printed object is achieved using additive processes, where an object is created by successively adding material layer by layer.
3D printing is the opposite of subtractive manufacturing which is the traditional approach to manufacturing where an object is created by starting with a larger piece of material. Then removing bits and pieces until the desired object shape remains. With additive manufacturing, there are no limits to the shapes or sizes that can be created since the only constraint is the build envelope of the printer being used.
There are currently several different technologies available for additive manufacturing including:
* Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
* Stereolithography (SLA)
* selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
* Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
* Electron Beam Melting (EBM).
Each technology has its own advantages and disadvantages which will be discussed in more detail below. In general, additive manufacturing offers many potential benefits over traditional subtractive manufacturing methods including:
- Lower production costs,
- Shorter lead times,
- Increased design freedom,
- Reduced waste,
- Improved product performance.
2. Subtractive Manufacturing
Subtractive Manufacturing is a process where parts are created by removing material from a solid block. The most common subtractive manufacturing technology is CNC machining. In CNC machining, a computer controls a cutting tool that removes material from the workpiece to create the desired shape.
Other subtractive manufacturing technologies include EDM (electrical discharge machining) and waterjet cutting. EDM uses electrical sparks to remove material from the workpiece, while waterjet cutting uses high-pressure water to cut through material.
3. Laser Cutting
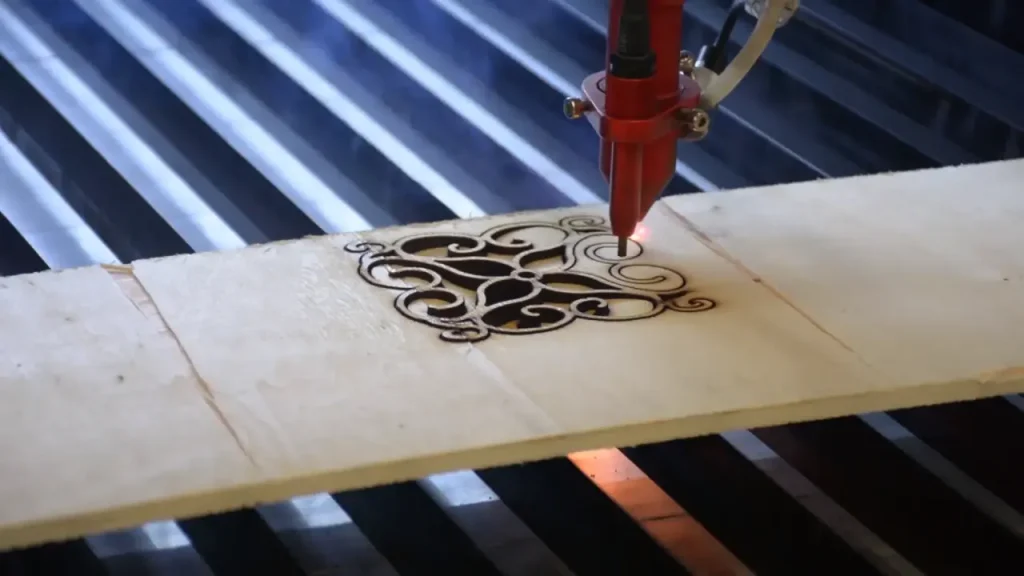

Laser cutting is a precise and versatile technology that can be used to cut a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, glass and wood. Laser cutting has a number of advantages over traditional cutting methods, including higher accuracy, faster cutting speeds, and the ability to cut complex shapes.
The Laser cutting is well suited for the rapidly growing field of 3D printing. 3D printing relies on the ability to create complex shapes quickly and accurately, making laser cutting an ideal technology for fabricating 3D-printed parts. Additionally, laser-cut parts are often used as templates or molds for 3D-printed parts, further increasing the efficiency of the manufacturing process.
4. DLP Digital Fabrication
The digital fabrication is a technology that allows factories to produce products without the need for human labor. This type of manufacturing is often referred to as “lights-out” or “unattended” manufacturing.
Digital fabrication technologies have been around for many years, but they are becoming increasingly important as manufacturers seek to reduce costs and increase efficiency. The most common digital fabrication technologies include 3D printing, laser cutting, and CNC machining.
3D printing is the process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital file. It is typically done using an additive process, where successive layers of material are added to create the desired shape. 3D printing has become increasingly popular in recent years due to its ability to create complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to create using traditional manufacturing methods.
Laser cutting is a digital fabrication technology that uses a laser to cut materials such as metal, plastic, or wood. Laser cutting is fast and accurate, making it ideal for prototyping and small-scale production runs.
CNC machining is a digital fabrication technology that uses computer-controlled tools to remove material from a workpiece. CNC machining can be used to create complex shapes and features that would be difficult or impossible to create using traditional manufacturing methods.
5. 3D Printing
In the next decade, digital fabrication technologies will become increasingly prevalent in manufacturing. These technologies include 3D printing, laser cutting and CNC machining.
3D printing is a process of creating three-dimensional objects from a digital file. The objects are created by successively layering material until the desired shape is achieved. 3D printing can be used to create products made from a variety of materials, including plastics, metals, and ceramics.
Laser cutting is a process of using a high-powered laser to cut through material. Laser cutting can be used to create intricate patterns and shapes that would be difficult to create with traditional methods.
CNC machining is a process of using computer-controlled machine tools to fabricate parts from a variety of materials. CNC machining can be used to create complex geometries with precise tolerances.
One Additional Fabrication Technology
6. Directed Energy Deposition
Directed energy deposition (DED) is a 3D printing technology that uses a focused laser or electron beam to melt and deposit material onto a substrate. DED systems are generally faster than other 3D printing technologies, and can be used to create large, complex parts with high accuracy.
DED systems can be used with a variety of materials, including metals, ceramics, and plastics. In recent years, the use of DED for fabricating metal parts has increased significantly, due to the technology’s ability to produce strong, heat-resistant parts with intricate geometries.
The main advantage of DED over other 3D printing technologies is its speed. DED systems can deposit material at rates of up to several kilograms per hour. It making them much faster than other technologies such as stereolithography (SLA) or selective laser melting (SLM).
Another advantage of DED is its flexibility. The technology can be used with a wide variety of materials, including metals, ceramics, and plastics. This makes it an ideal choice for fabricating parts with complex geometries or for applications where multiple material types are required.
Finally, DED systems are generally more accurate than other 3D printing technologies. This high accuracy is due to the fact that the laser or electron beam is directed very precisely onto the substrate. As a result, parts fabricated using DED tend to have tighter tolerances and smoother surfaces than those produced by other.
These technologies will dominate manufacturing & construction or BIM industry in the next 5 years. If you are ready to start your career in BIM, check out our previous blog.
Conclusion
There’s no doubt that fabrication technologies are rapidly evolving, and it’s exciting to think about what the next 5 years will bring. We can’t wait to see how these new technologies will change the manufacturing landscape and we’ll be sure to keep you updated on all the latest developments. In the meantime, if you’re looking for ways to stay ahead of the curve, investing in one or more of these promising technologies is a good place to start.
Follow us to stay updated on LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram and Twitter.
